New York Times, March 4th 2019 –
By Kendra Pierre-Louis and Nadja Popovich
When deadly heat waves hit on land, we hear about them. But the oceans can have heat waves, too. They are now happening far more frequently than they did last century and are harming marine life, according to a new study.

The average number of marine heat wave days for the period 1987-2016, compared to the average for 1925-1954. Orange-red range indicates 18-36+ more marine heat wave days compared to the mid-20th century.
Source: Nature Climate Change | By The New York Times
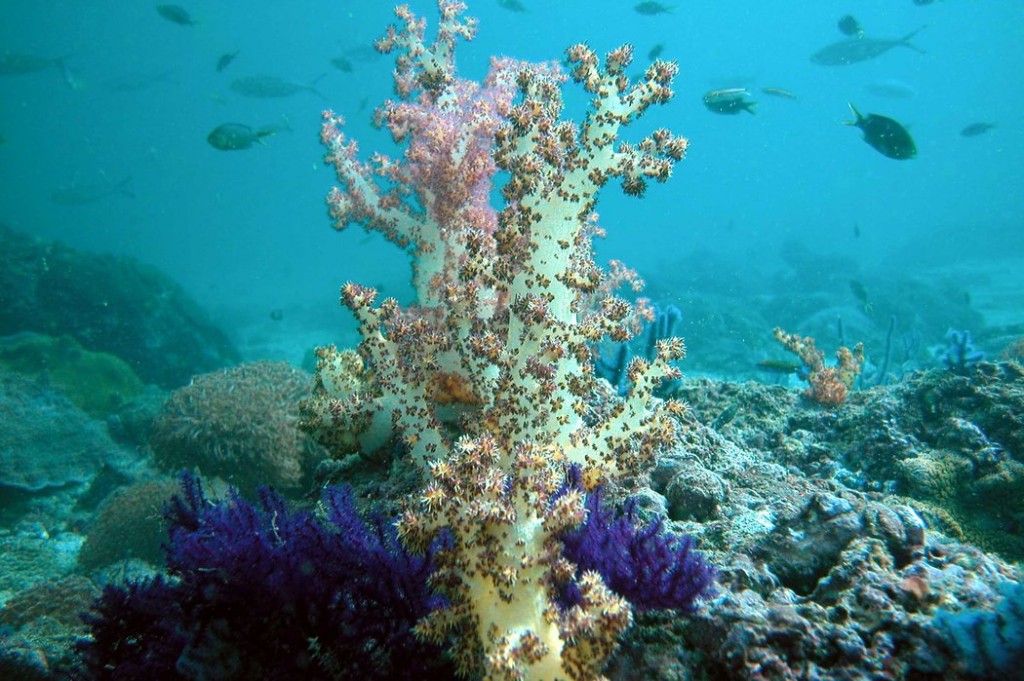
The study, published Monday in the journal Nature Climate Change, looked at the impact of marine heat waves on the diversity of life in the ocean. From coral reefs to kelp forests to sea grass beds, researchers found that these heat waves were destroying the framework of many ocean ecosystems.
Marine heat waves are said to occur when sea temperatures are much warmer than normal for at least five consecutive days.
Scientists estimate that the oceans have absorbed more than 90 percent of the heat trapped by excess greenhouse gases since midcentury. Humans have added these gases to the atmosphere largely by burning fossil fuels, like coal and natural gas, for energy.
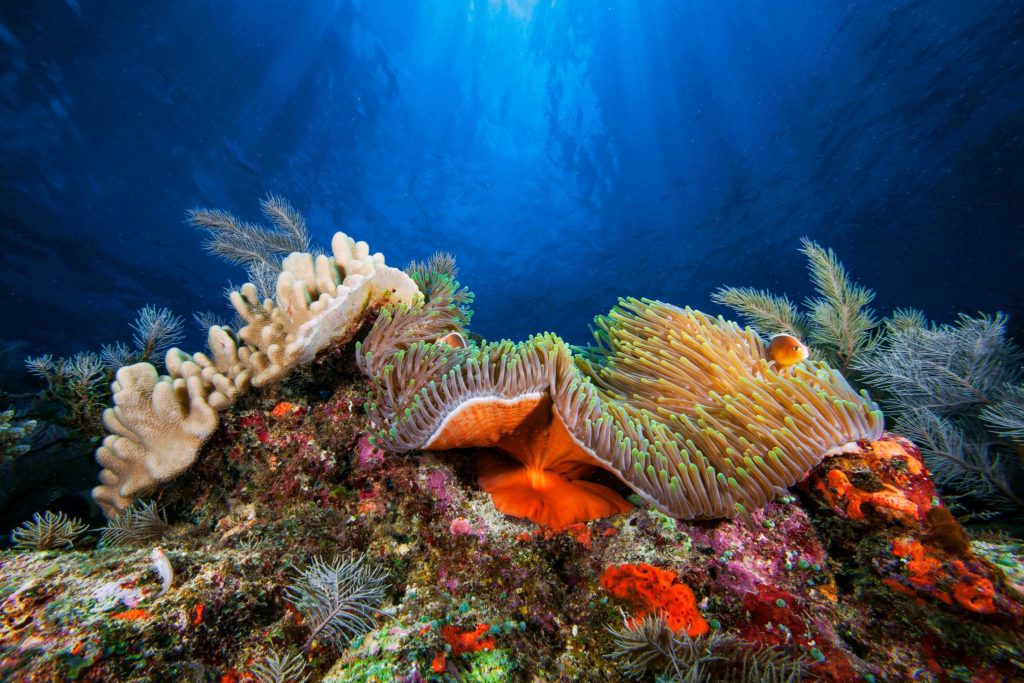

An estimated one billion people depend on coral reefs, which are highly sensitive to temperature, for food or income. Credit Gabriel Barathieu/Biosphoto/Minden Pictures
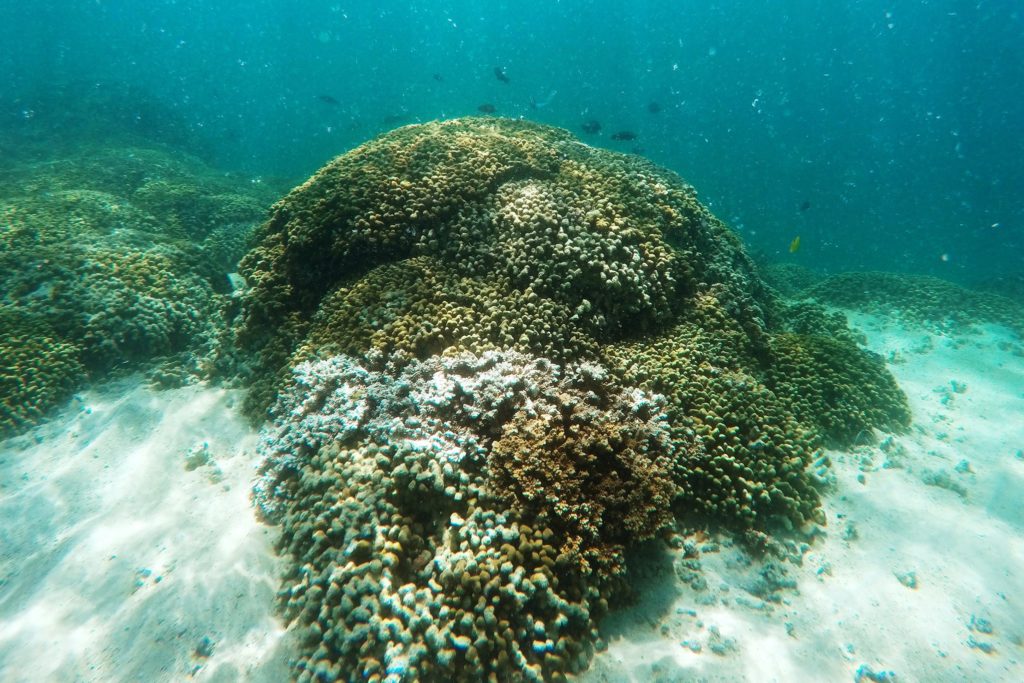

Bleached coral in Kaneohe Bay off Oahu, Hawaii. Credit Caleb Jones/AP
An earlier study by some of the same researchers found that, from 1925 to 2016, marine heat waves became, on average, 34 percent more frequent and 17 percent longer. Over all, there were 54 percent more days per year with marine heat waves globally.
The most severe years tended to be El Niño years. Warmer ocean temperatures are one of the characteristics of an El Niño pattern.
“There’s also some indication that El Niños have been getting more extreme with climate change,” said Eric C. J. Oliver, an assistant professor of physical oceanography at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia, who was a co-author of the study. But regional marine heat waves can happen even without an El Niño, he said.

 are absorbing increasing amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, so much so that the chemical balance of our oceans and coastal waters is changing and a growing threat to marine ecosystems. Over the past 200 years, the world’s seas have absorbed more than 150 billion metric tons of carbon from human activities. Currently, that’s a worldwide average of 15 pounds per person a week, enough to fill a coal train long enough to encircle the equator 13 times every year.
are absorbing increasing amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, so much so that the chemical balance of our oceans and coastal waters is changing and a growing threat to marine ecosystems. Over the past 200 years, the world’s seas have absorbed more than 150 billion metric tons of carbon from human activities. Currently, that’s a worldwide average of 15 pounds per person a week, enough to fill a coal train long enough to encircle the equator 13 times every year.